Have you ever wondered what the difference is between artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics?
Are they the same thing, or are they completely different fields of technology?
How do they relate to each other, and what are some examples of AI robots?
In this blog post, we will answer these questions and more. We will explain what AI and robotics are, how they differ, and how they overlap.
We will also look at some of the current and future applications of AI robots in various domains, such as healthcare, education, entertainment, and industry.
By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of the fascinating world of AI and robotics, and how they are shaping our lives and society.
What is AI?
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, mimics human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks like understanding language, recognizing faces, making decisions, and learning from data.

There are two primary AI types:
Narrow AI: Specializes in specific tasks like speech and image recognition.
General AI: Theoretical AI with human-like intellectual abilities, still unrealized.
AI has two main approaches:
Symbolic AI is the approach that uses symbols and rules to represent and manipulate knowledge.
Sub-symbolic AI is the approach that uses numerical values and mathematical models to simulate neural networks and learning processes.
What is Robotics?
Robotics is a branch of technology that deals with physical robots. Robots are programmable machines that are usually able to carry out a series of actions autonomously, or semi-autonomously.
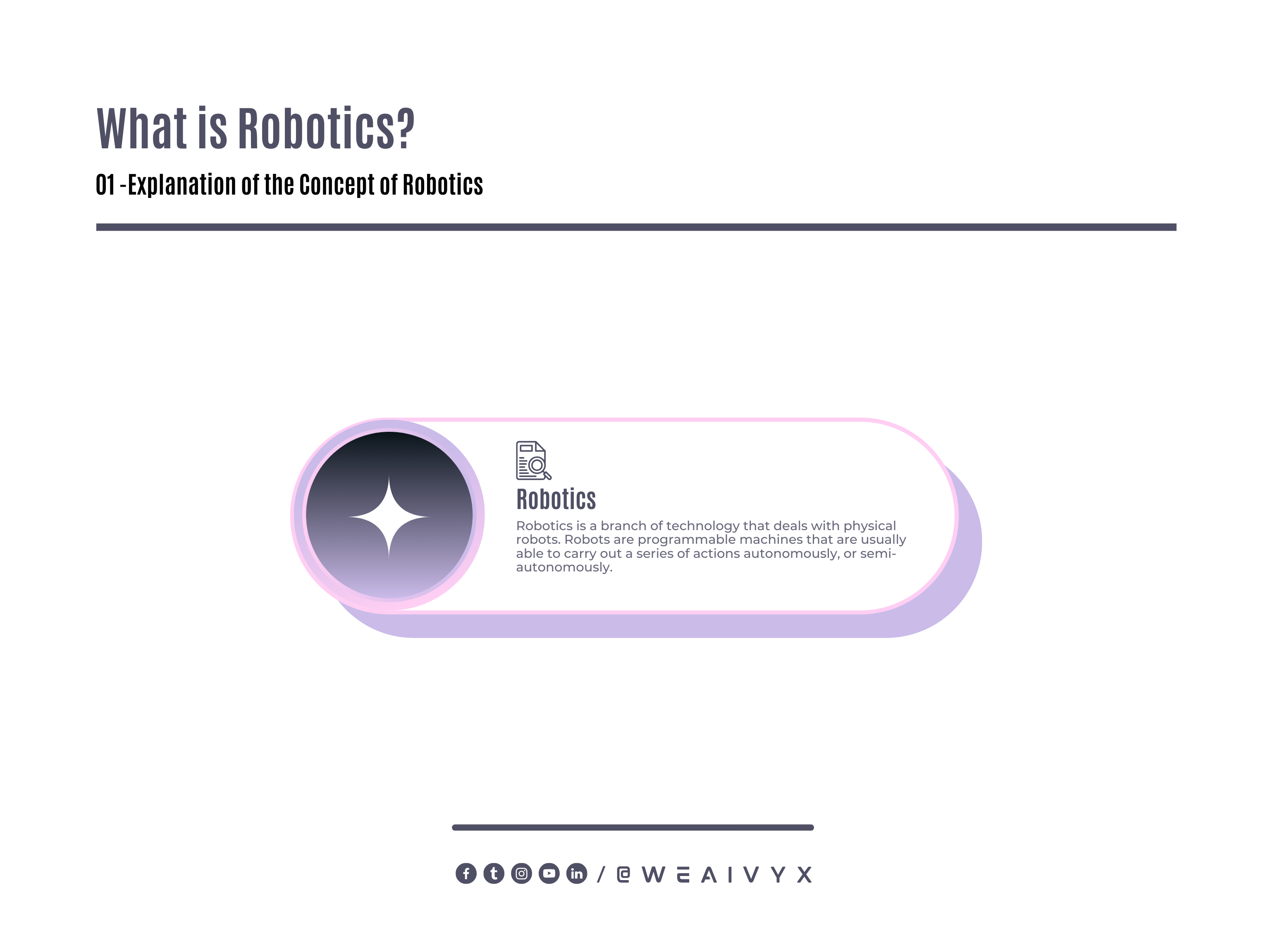
Robots interact with the physical world via sensors and actuators. Sensors are devices that detect information from the environment, such as light, sound, temperature, or distance.
Actuators are devices that produce physical movements or forces, such as motors, wheels, arms, or grippers.
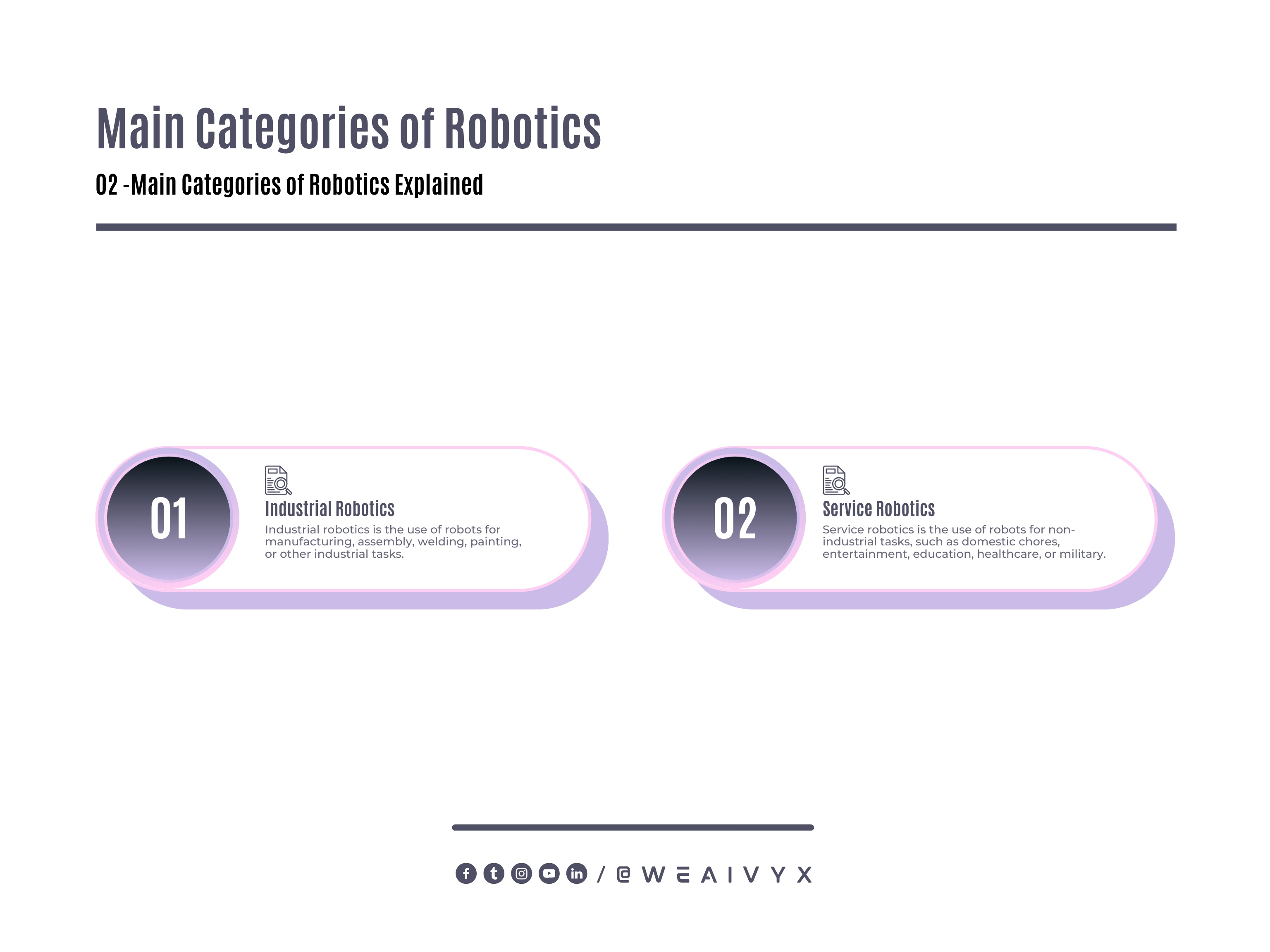
Robotics can be divided into two main categories:
Industrial Robotics
Service Robotics
Industrial Robotics is the use of robots for manufacturing, assembly, welding, painting, or other industrial tasks.
Service Robotics is the use of robots for non-industrial tasks, such as domestic chores, entertainment, education, healthcare, or military.
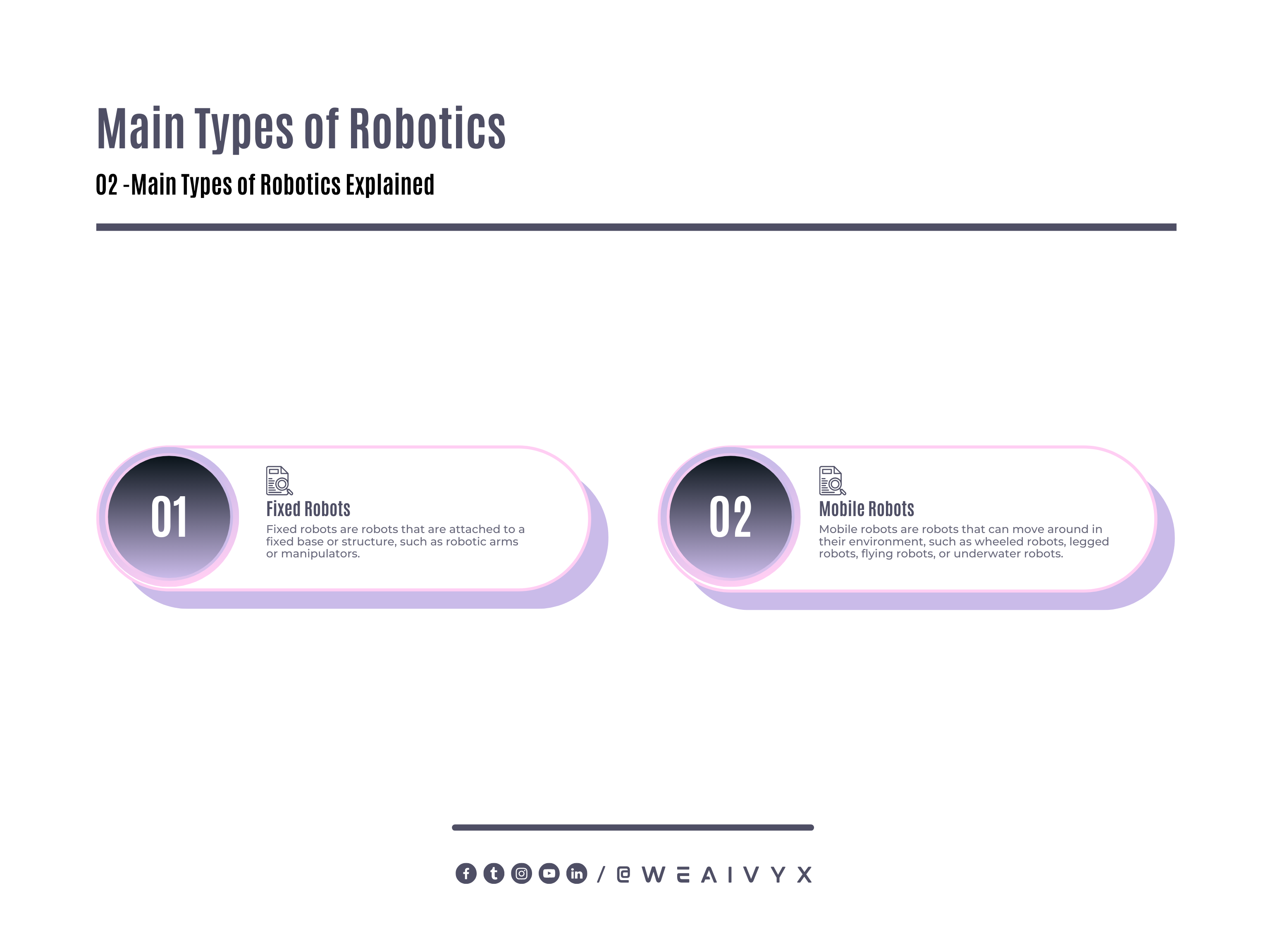
Robotics can also be divided into two main types:
Fixed Robots
Mobile Robots
Fixed Robots are robots that are attached to a fixed base or structure, such as robotic arms or manipulators.
Mobile Robots are robots that can move around in their environment, such as wheeled robots, legged robots, flying robots, or underwater robots.
How do AI and Robotics Differ?
AI and robotics are related but distinct fields of computer science.
They differ in several aspects:
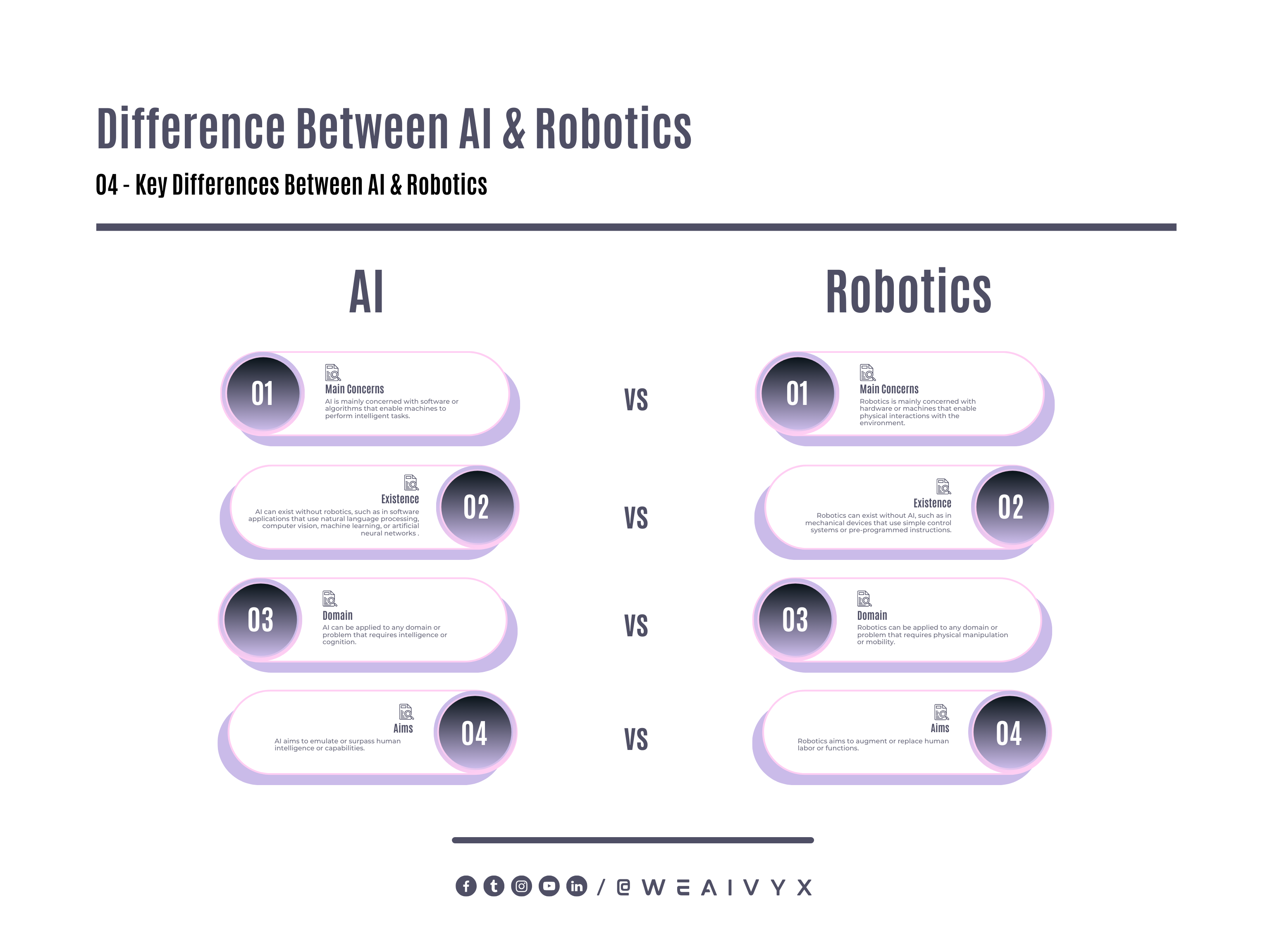
AI is mainly concerned with software or algorithms that enable machines to perform intelligent tasks.
Robotics is mainly concerned with hardware or machines that enable physical interactions with the environment.
AI can exist without robotics, such as in software applications that use natural language processing (NLP), computer vision (CV), machine learning (ML), or artificial neural networks (ANN).
Robotics can exist without AI, such as in mechanical devices that use simple control systems or pre-programmed instructions.
AI can be applied to any domain or problem that requires intelligence or cognition.
Robotics can be applied to any domain or problem that requires physical manipulation or mobility.
AI aims to emulate or surpass human intelligence or capabilities.
Robotics aims to augment or replace human labor or functions.
How to do AI and Robotics Overlap?
AI and robotics overlap when they are combined to create artificially intelligent robots.
These are robots that use AI algorithms and models to execute more than just a repetitive series of movements and increase their autonomy.
Autonomy is the degree to which a robot can perform its tasks without human intervention or supervision.
Artificially intelligent robots can use various types of AI techniques depending on their goals and capabilities:
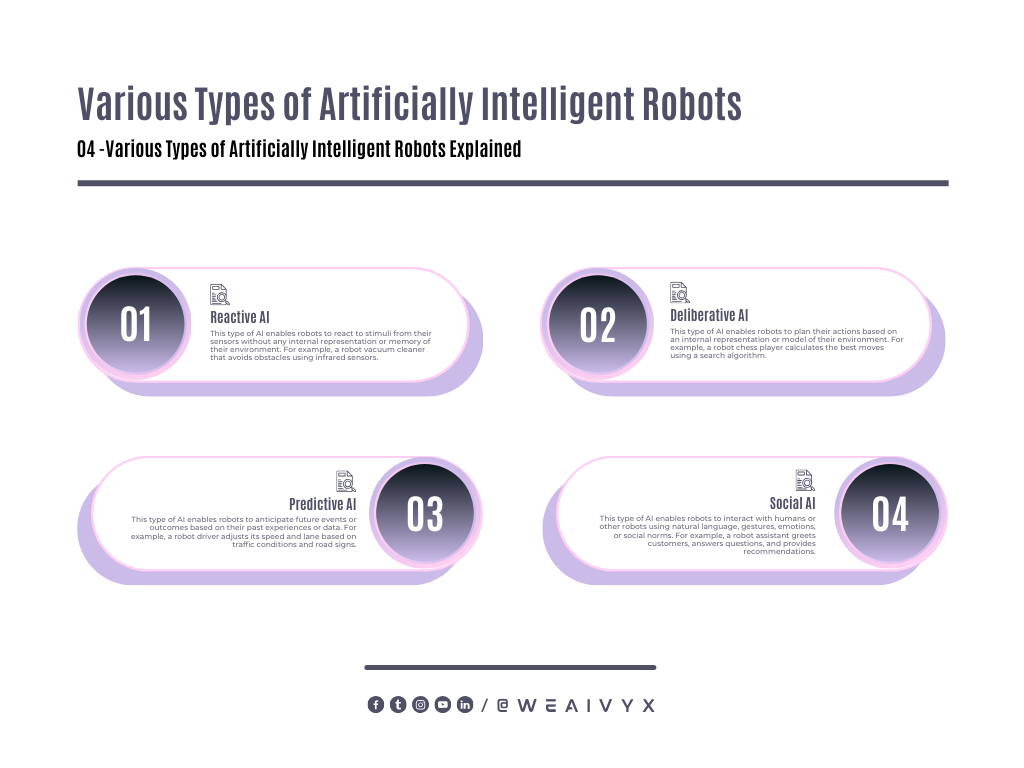
Reactive AI: This type of AI enables robots to react to stimuli from their sensors without any internal representation or memory of their environment.
For example, a robot vacuum cleaner that avoids obstacles using infrared sensors.
Deliberative AI: This type of AI enables robots to plan their actions based on an internal representation or model of their environment.
For example, a robot chess player calculates the best moves using a search algorithm.
Predictive AI: This type of AI enables robots to anticipate future events or outcomes based on their past experiences or data.
For example, a robot driver adjusts its speed and lane based on traffic conditions and road signs.
Social AI: This type of AI enables robots to interact with humans or other robots using natural language, gestures, emotions, or social norms.
For example, a robot assistant greets customers, answers questions, and provides recommendations.
What Are Some Examples of AI Robots?
AI robots are becoming more common and advanced in various domains and applications.
Here are some examples of AI robots that you may have heard of or encountered:
Sophia
Sophia is a humanoid robot that was developed by Hanson Robotics in Hong Kong.
Sophia can engage in natural conversations, express emotions, and make facial expressions.
Sophia was granted citizenship by Saudi Arabia in 2023, making her the first robot to have legal status.
Spot
Spot is a four-legged robot that was developed by Boston Dynamics in the USA.
Spot can walk, run, climb stairs, jump, and carry loads.
Spot can also navigate complex terrains and avoid obstacles using cameras and sensors.
The spot has been used for various purposes, such as inspection, delivery, entertainment, and military.
Pepper
Pepper is a humanoid robot that was developed by SoftBank Robotics in Japan.
Pepper can recognize faces, emotions, and speech.
Pepper can also dance, play games, and tell jokes.
Pepper is designed to be a social companion for humans, especially in retail, hospitality, education, and healthcare settings.
RoboBee
RoboBee is a tiny flying robot that was developed by Harvard University in the USA.
RoboBee can flap its wings at a high frequency and perform controlled flight maneuvers.
RoboBee can also perch on surfaces using electrostatic adhesion.
RoboBee is inspired by the biology and behavior of bees and could be used for pollination, surveillance, or exploration.
AlphaGo
AlphaGo is a computer program that was developed by DeepMind in the UK.
AlphaGo uses deep neural networks and reinforcement learning to play the board game Go.
AlphaGo became the first program to defeat a professional human Go player in 2015 and later defeated the world champion Lee Sedol in March 2016.

Conclusion
AI and robotics are two different but related fields of technology that have many applications and implications for our society.
AI is the intelligence demonstrated by machines, while robotics is the physical interaction of machines with the environment.
AI and robotics overlap when they are combined to create artificially intelligent robots that can perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously.
AI robots can use various types of AI techniques depending on their goals and capabilities, such as reactive AI, deliberative AI, predictive AI, or social AI.
AI robots can also be classified into different categories based on their domains or functions, such as industrial robotics or service robotics.
AI robots are becoming more common and advanced in various domains and applications, such as healthcare, education, entertainment, and industry.
Some examples of AI robots are Sophia, Spot, Pepper, RoboBee, and AlphaGo.
We hope you enjoyed this blog post and learned something new about AI and robotics. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below. We would love to hear from you!
Also, if you liked this post, please share it with your friends or colleagues who might be interested in this topic.