Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the field of medicine, especially in the area of diagnosis.
AI algorithms can analyze medical images, laboratory tests, symptoms, and other data to provide diagnoses and recommendations for treatment.
But how do they compare with human doctors in terms of accuracy and reliability? And what are the benefits and challenges of using AI for medical diagnosis?
In this blog post, we will explore these questions and more, based on the latest research and evidence.
What is AI and How Does it Work in Medical Diagnosis?
AI is the ability of a machine or a software program to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity.
Two main types of AI
Narrow AI
Narrow AI is focused on a specific task or domain, such as playing chess, recognizing faces, or diagnosing diseases.
General AI
General AI is the hypothetical ability of a machine to perform any intellectual task that a human can do.
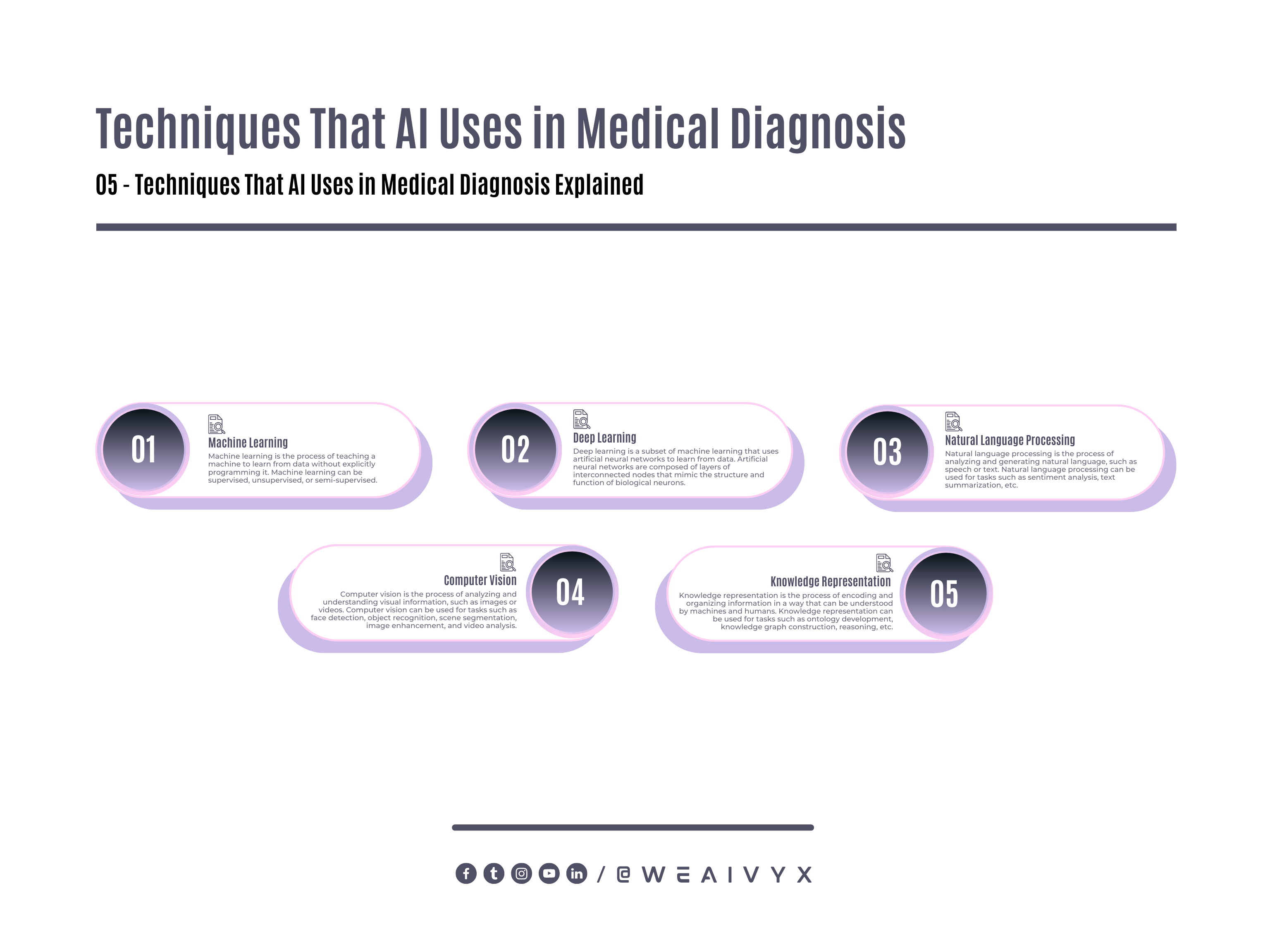
AI works in medical diagnosis by using various techniques, such as machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and knowledge representation.
The following techniques enable AI to learn from data, extract patterns, generate hypotheses, and provide solutions.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is the process of teaching a machine to learn from data without explicitly programming it.
Machine learning can be supervised, unsupervised, or semi-supervised.
Supervised Machine Learning
Supervised machine learning is when the machine learns from labeled data, such as images with annotations or texts with categories.
Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised machine learning is the process in which the machine learns from unlabeled data, such as images without annotations or texts without categories.
Semi-Supervised Machine Learning
Semi-supervised machine learning is when the machine learns from a combination of labeled and unlabeled data.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from data.
Artificial neural networks are composed of layers of interconnected nodes that mimic the structure and function of biological neurons.
Deep learning can handle complex and high-dimensional data, such as medical images or genomic sequences.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing is the process of analyzing and generating natural language, such as speech or text.
Natural language processing can be used for tasks such as sentiment analysis, text summarization, question answering, chatbots, and speech recognition.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is the process of analyzing and understanding visual information, such as images or videos.
Computer vision can be used for tasks such as face detection, object recognition, scene segmentation, image enhancement, and video analysis.
Knowledge Representation
Knowledge representation is the process of encoding and organizing information in a way that can be understood by machines and humans.
Knowledge representation can be used for tasks such as ontology development, knowledge graph construction, reasoning, inference, and explanation.
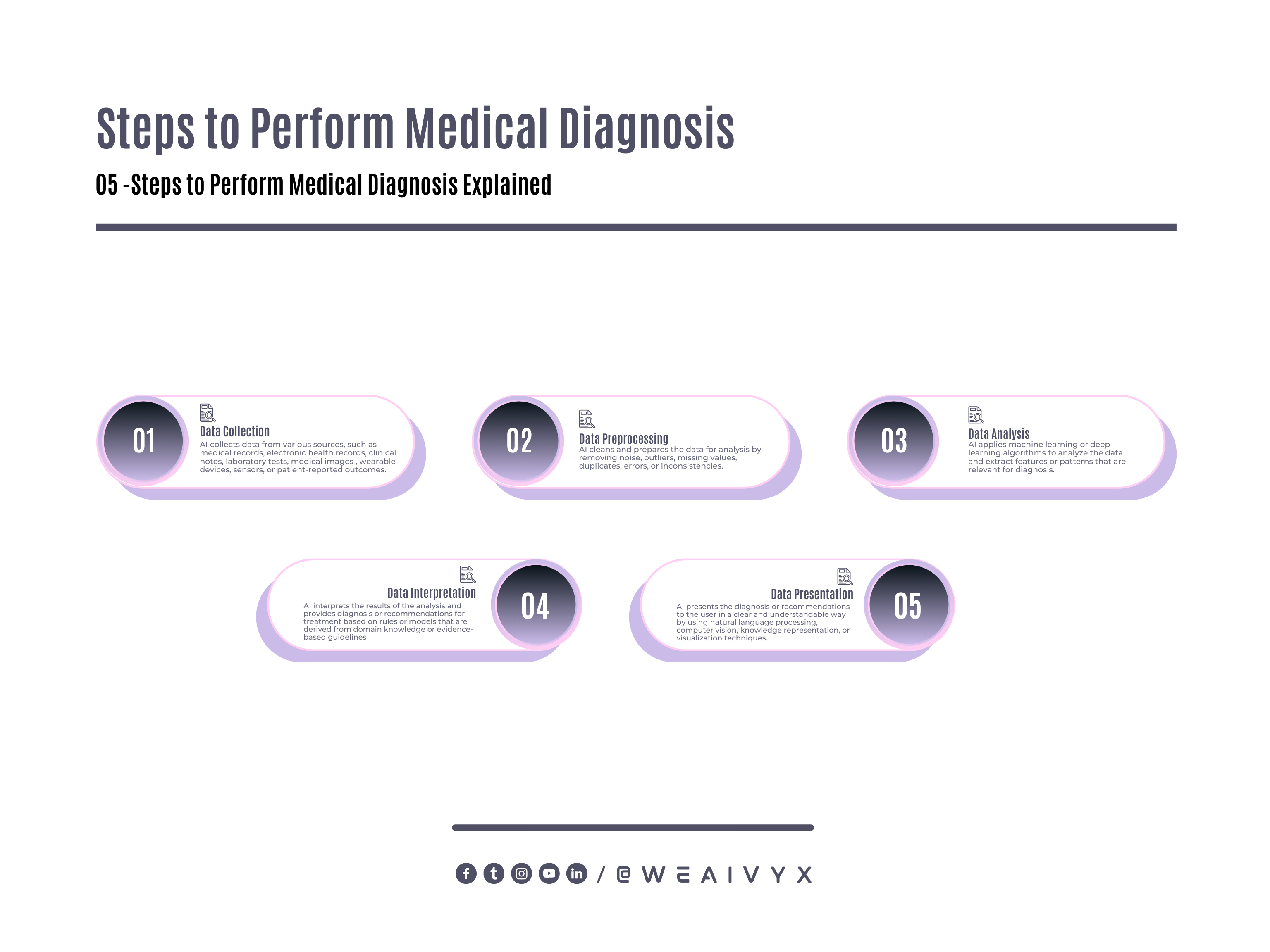
AI can use these techniques to perform medical diagnosis by following these steps:
Data Collection
AI collects data from various sources, such as medical records, electronic health records (EHRs), clinical notes, laboratory tests, medical images (such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans), wearable devices (such as smartwatches or fitness trackers), sensors (such as blood pressure monitors or glucose meters), or patient-reported outcomes (such as symptoms or feedback).
Data Preprocessing
AI cleans and prepares the data for analysis by removing noise, outliers, missing values, duplicates, errors, or inconsistencies.
Data Analysis
AI applies machine learning or deep learning algorithms to analyze the data and extract features or patterns that are relevant for diagnosis.
Data Interpretation
AI interprets the results of the analysis and provides diagnosis or recommendations for treatment based on rules or models that are derived from domain knowledge or evidence-based guidelines.
Data Presentation
AI presents the diagnosis or recommendations to the user (such as a doctor, a patient, or a caregiver) clearly and understandably by using natural language processing, computer vision, knowledge representation, or visualization techniques.
How Accurate is AI in Medical Diagnosis?
AI has shown impressive accuracy and sensitivity in the identification of imaging abnormalities and promises to enhance tissue-based detection and characterization.
According to a study, AI can correctly diagnose disease in 87% of cases, whereas detection by healthcare professionals yielded an 86% accuracy rate.
The specificity for deep learning algorithms was 93%, compared with humans’ at 91%. However, biases may exaggerate AI performance.
Another study compared the diagnostic accuracy of an AI chatbot with human doctors for the common symptoms of 10 diseases.
The AI chatbot achieved an accuracy of 90.32%, while the human doctors achieved an accuracy of 80.64%.
The AI chatbot also had a higher sensitivity (94.12%) and specificity (88.89%) than the human doctors (88.24% and 76.19%, respectively).
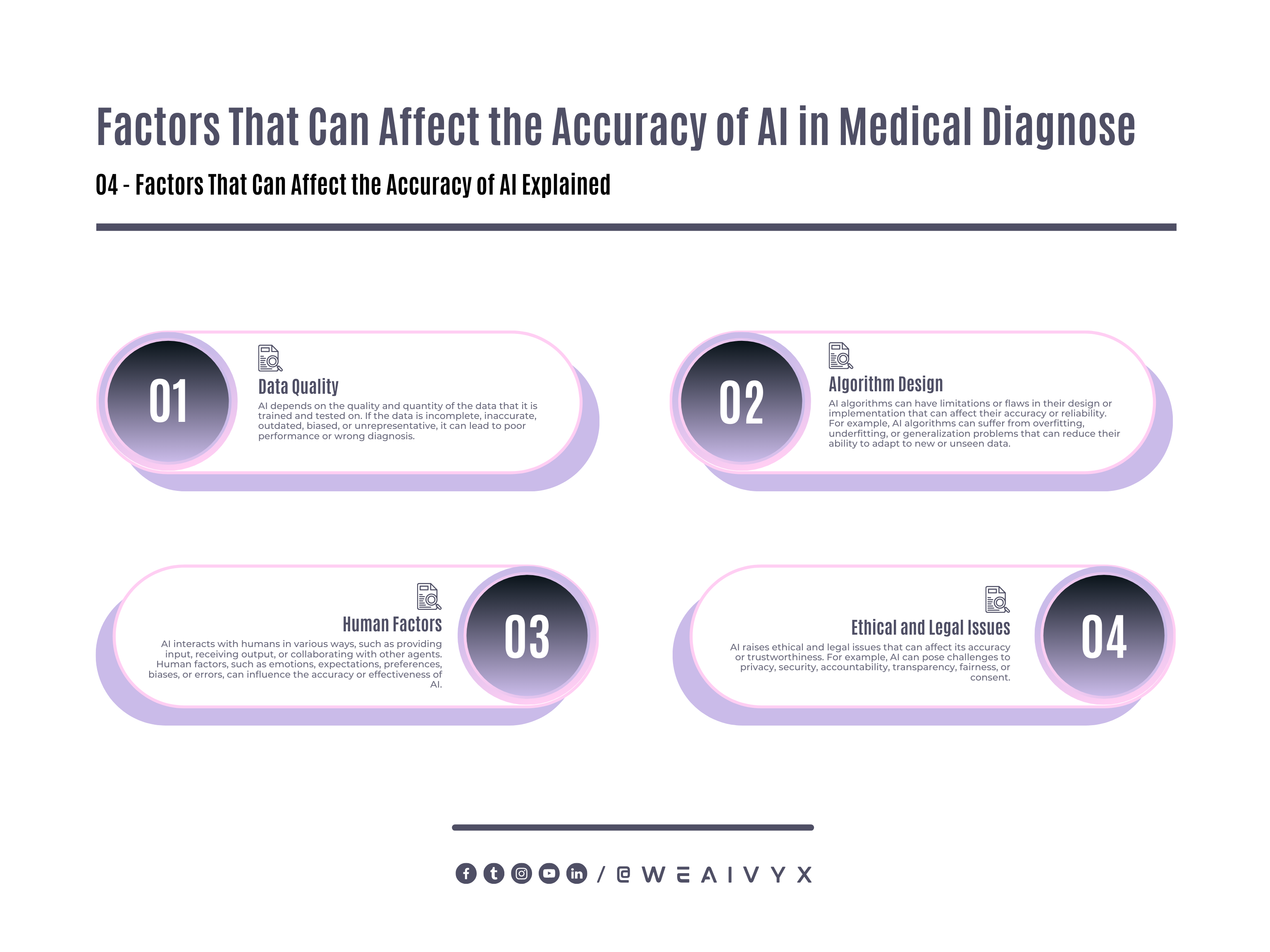
However, AI is not flawless and can make mistakes or errors in medical diagnosis. Some of the factors that can affect the accuracy of AI are:
Data Quality: AI depends on the quality and quantity of the data that it is trained and tested on. If the data is incomplete, inaccurate, outdated, biased, or unrepresentative, it can lead to poor performance or wrong diagnosis.
Algorithm Design: AI algorithms can have limitations or flaws in their design or implementation that can affect their accuracy or reliability.
For example, AI algorithms can suffer from overfitting, underfitting, or generalization problems that can reduce their ability to adapt to new or unseen data.
Human Factors: AI interacts with humans in various ways, such as providing input, receiving output, or collaborating with other agents. Human factors, such as emotions, expectations, preferences, biases, or errors, can influence the accuracy or effectiveness of AI.
Ethical and Legal Issues: AI raises ethical and legal issues that can affect its accuracy or trustworthiness.
For example, AI can pose challenges to privacy, security, accountability, transparency, fairness, or consent.
Therefore, AI should not be seen as a replacement for human doctors, but rather as a tool or a partner that can augment and assist them in medical diagnosis.
What are the Benefits and Challenges of Using AI for Medical Diagnosis?
AI has many benefits and challenges for medical diagnosis.
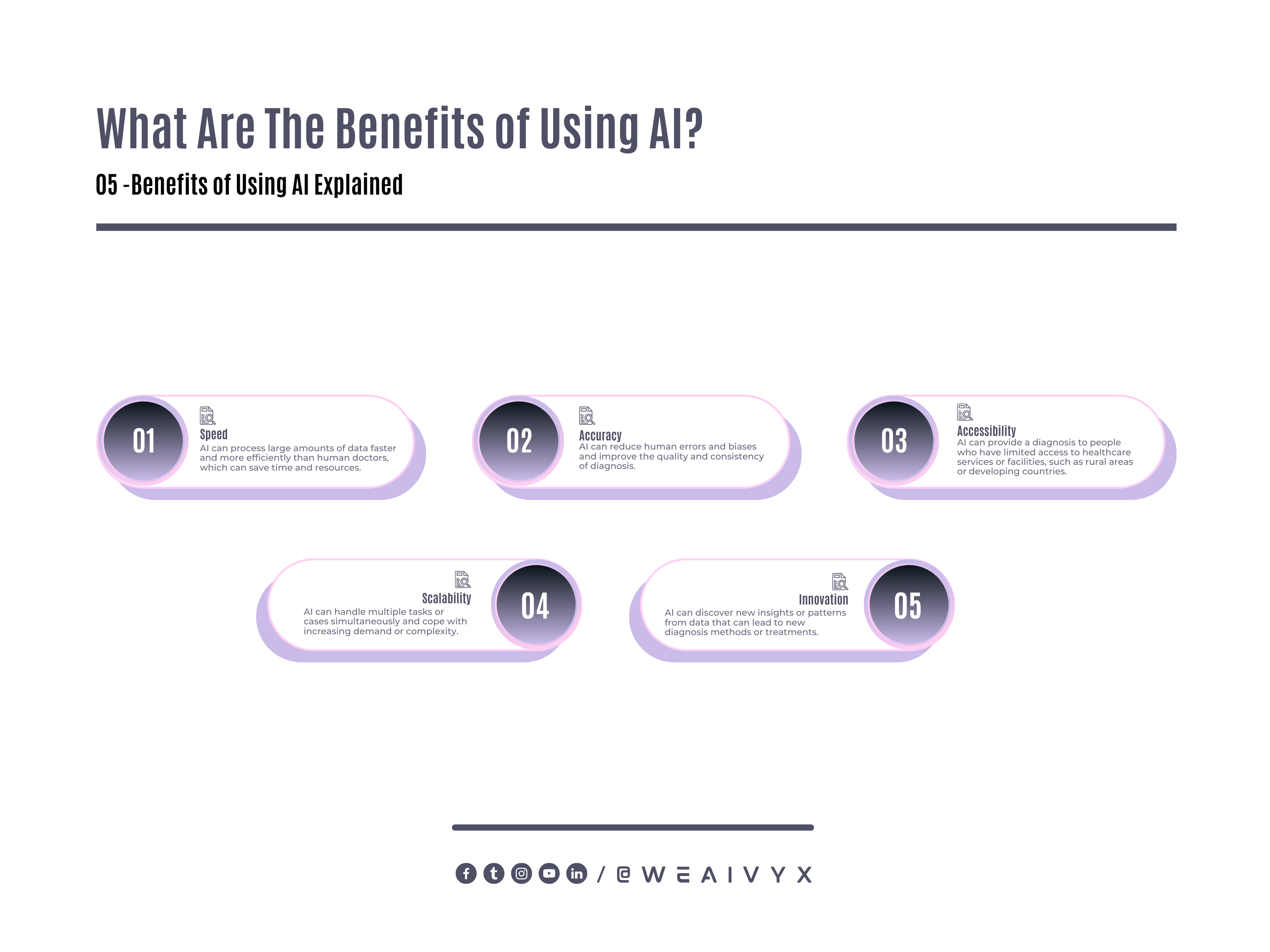
Benefits of AI
Speed: AI can process large amounts of data faster and more efficiently than human doctors, which can save time and resources.
Accuracy: AI can reduce human errors and biases and improve the quality and consistency of diagnosis.
Accessibility: AI can provide a diagnosis to people who have limited access to healthcare services or facilities, such as rural areas or developing countries.
Scalability: AI can handle multiple tasks or cases simultaneously and cope with increasing demand or complexity.
Innovation: AI can discover new insights or patterns from data that can lead to new diagnosis methods or treatments.
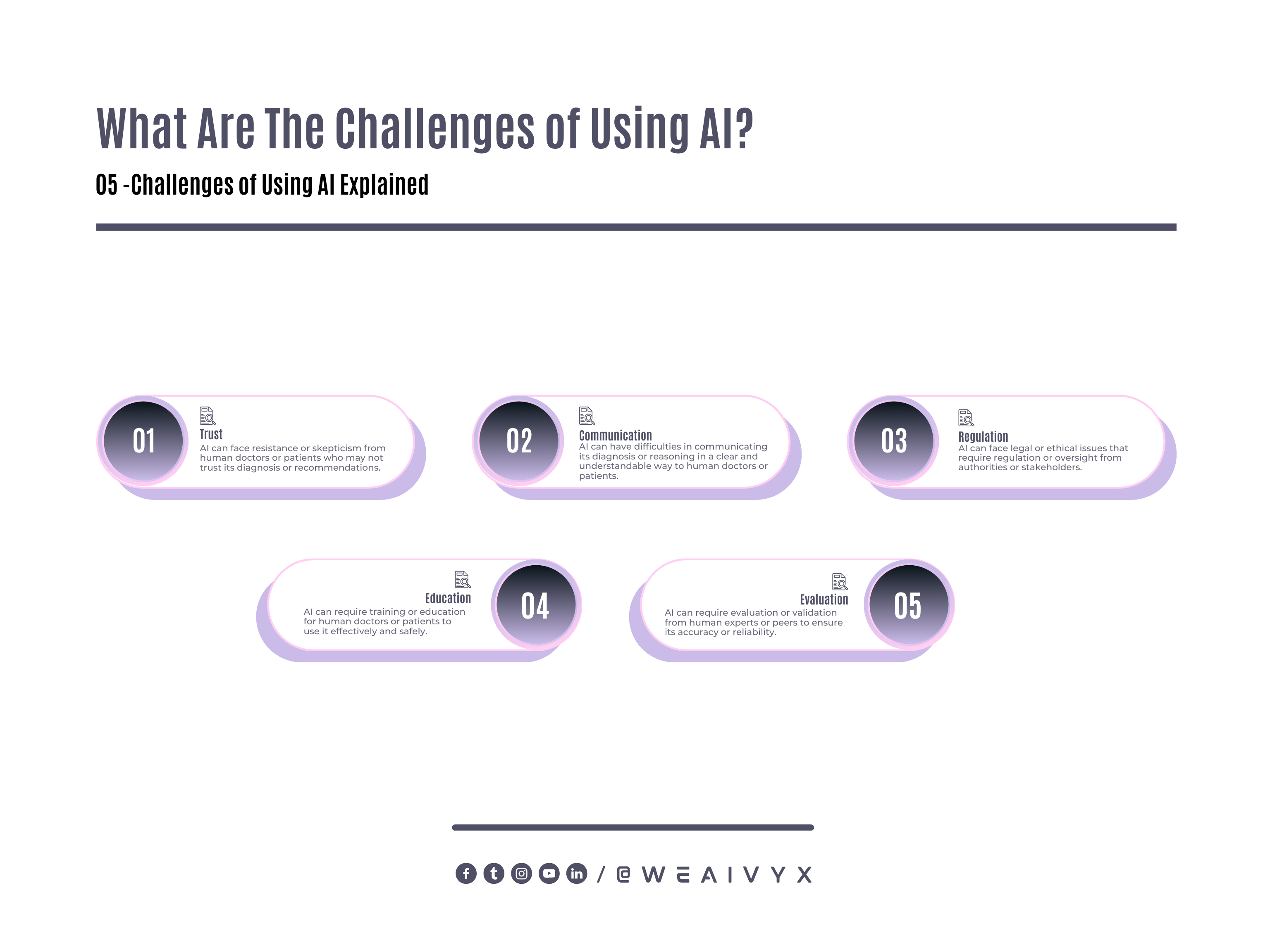
Challenges of AI
Trust: AI can face resistance or skepticism from human doctors or patients who may not trust its diagnosis or recommendations.
Communication: AI can have difficulties in communicating its diagnosis or reasoning clearly and understandably to human doctors or patients.
Regulation: AI can face legal or ethical issues that require regulation or oversight from authorities or stakeholders.
Education: AI can require training or education for human doctors or patients to use it effectively and safely.
Evaluation: AI can require evaluation or validation from human experts or peers to ensure its accuracy or reliability.
What are the Latest Studies and Research on AI vs. Doctors in Medical Diagnosis?
AI vs Doctors in medical diagnosis is a hot topic of research and innovation, as many studies and projects are being conducted to explore the potential and challenges of AI in this field.
Here are some of the latest studies and research on AI vs. Doctors in medical diagnosis:
Study Published in 2019
A study published in 2019 compared the diagnostic performance of AI and clinicians for 14 common diseases, such as pneumonia, asthma, urinary tract infection, and sinusitis.
The study used a dataset of 6,806 cases from a Chinese online healthcare platform, where patients submitted their symptoms and received diagnoses from both AI and clinicians.
The study found that AI achieved an overall accuracy of 82%, which was comparable to that of clinicians (81%).
However, AI performed better than clinicians for some diseases, such as pneumonia (91% vs. 83%), while clinicians performed better than AI for some diseases, such as sinusitis (88% vs. 80%).
Study Published in 2020
A study published in 2020 compared the diagnostic accuracy of an AI chatbot with human doctors for the common symptoms of 10 diseases, such as headache, chest pain, cough, and fever.
The study used a dataset of 1,248 cases from a UK-based online healthcare platform, where patients submitted their symptoms and received diagnoses from both AI and doctors.
The study found that the AI chatbot achieved an accuracy of 90.32%, while the human doctors achieved an accuracy of 80.64%.
The AI chatbot also had a higher sensitivity (94.12%) and specificity (88.89%) than the human doctors (88.24% and 76.19%, respectively).
Study Published in 2021
A study published in 2021 compared the diagnostic performance of AI and radiologists for breast cancer screening using mammograms.
The study used a dataset of 29,807 cases from a US-based healthcare system, where patients underwent mammograms and received diagnoses from both AI and radiologists.
The study found that AI achieved a sensitivity of 92%, which was higher than that of radiologists (87%).
However, AI had a lower specificity (88%) than radiologists (91%), meaning that AI had more false positives than radiologists.
Project Launched in 2021
A project launched in 2021 aims to develop an AI system that can diagnose COVID-19 using chest X-rays.
The project is led by researchers from the University of Cambridge and Imperial College London and involves collaboration with hospitals in India, Mexico, and Brazil.
The project hopes to create an AI system that can provide a fast and accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 for low-resource settings, where access to testing kits or CT scans may be limited or unavailable.
These are just some examples of the ongoing studies and research on AI vs. Doctors in medical diagnosis.
There are many more studies and research that are exploring different aspects of AI in medical diagnoses, such as its impact on patient outcomes, satisfaction, trust, ethics, or cost-effectiveness.
What is the Future of AI in Healthcare?
The future of AI in healthcare is promising and exciting, but also uncertain and complex. AI is not a magic bullet that can solve all the problems or challenges in healthcare.
Nor is it a threat that can replace or harm human doctors or patients. Rather, it is a tool that can augment and complement human capabilities and intelligence.
The future of AI in healthcare will depend on how we use it wisely and responsibly, how we balance its benefits and risks, how we address its limitations and challenges, and how we integrate it with other technologies and innovations.
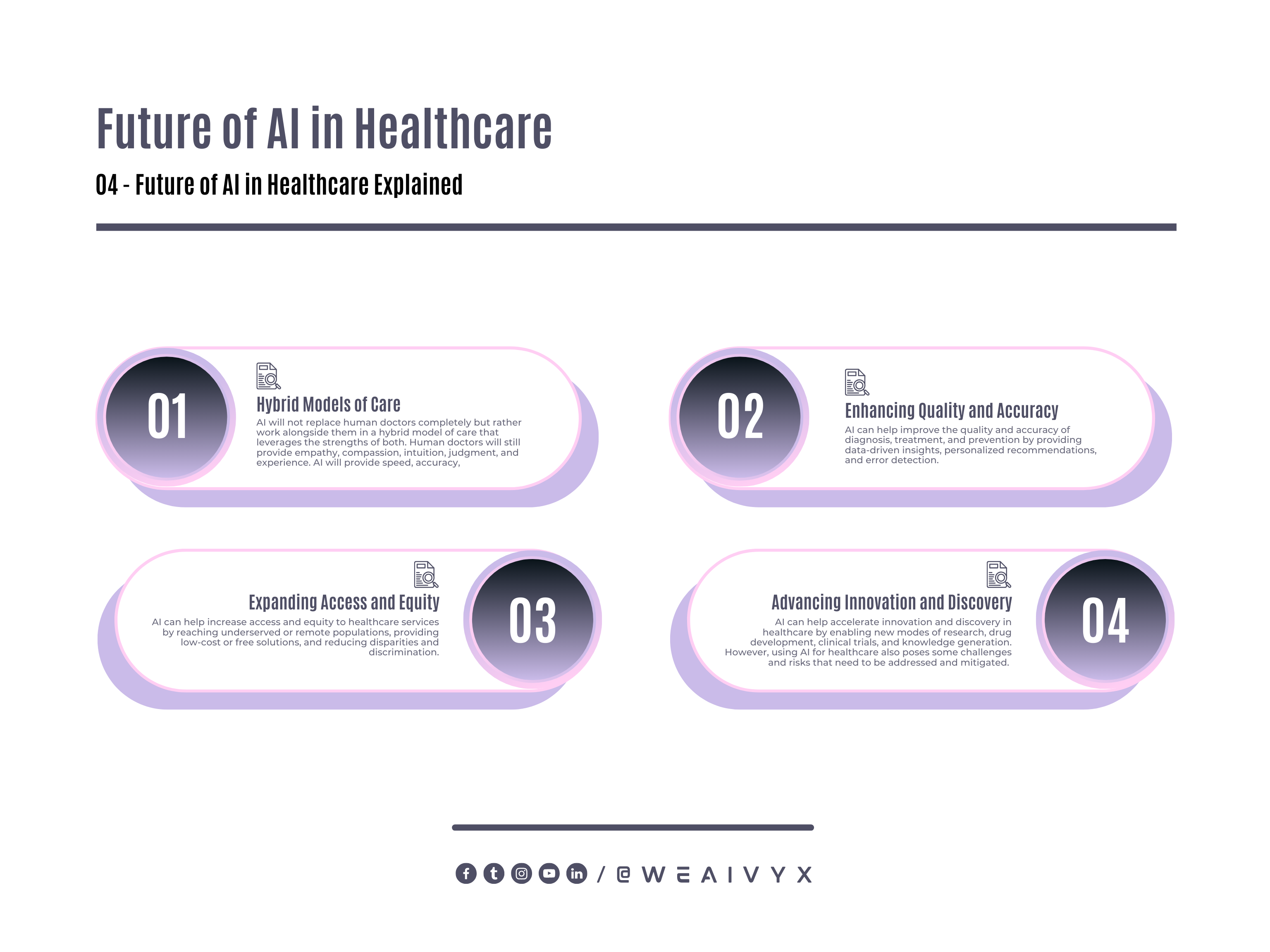
Some of the possible scenarios or trends that may shape the future of AI in healthcare are:
Hybrid Models of Care
AI will not replace human doctors completely but rather work alongside them in a hybrid model of care that leverages the strengths of both.
Human doctors will still provide empathy, compassion, intuition, judgment, and experience. AI will provide speed and accuracy.
Enhancing Quality and Accuracy
AI can help improve the quality and accuracy of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention by providing data-driven insights, personalized recommendations, and error detection.
Expanding Access and Equity
AI can help increase access and equity to healthcare services by reaching underserved or remote populations, providing low-cost or free solutions, and reducing disparities and discrimination.
Advancing Innovation and Discovery
AI can help accelerate innovation and discovery in healthcare by enabling new modes of research, drug development, clinical trials, and knowledge generation.
However, using AI for healthcare also poses some challenges and risks that need to be addressed and mitigated.
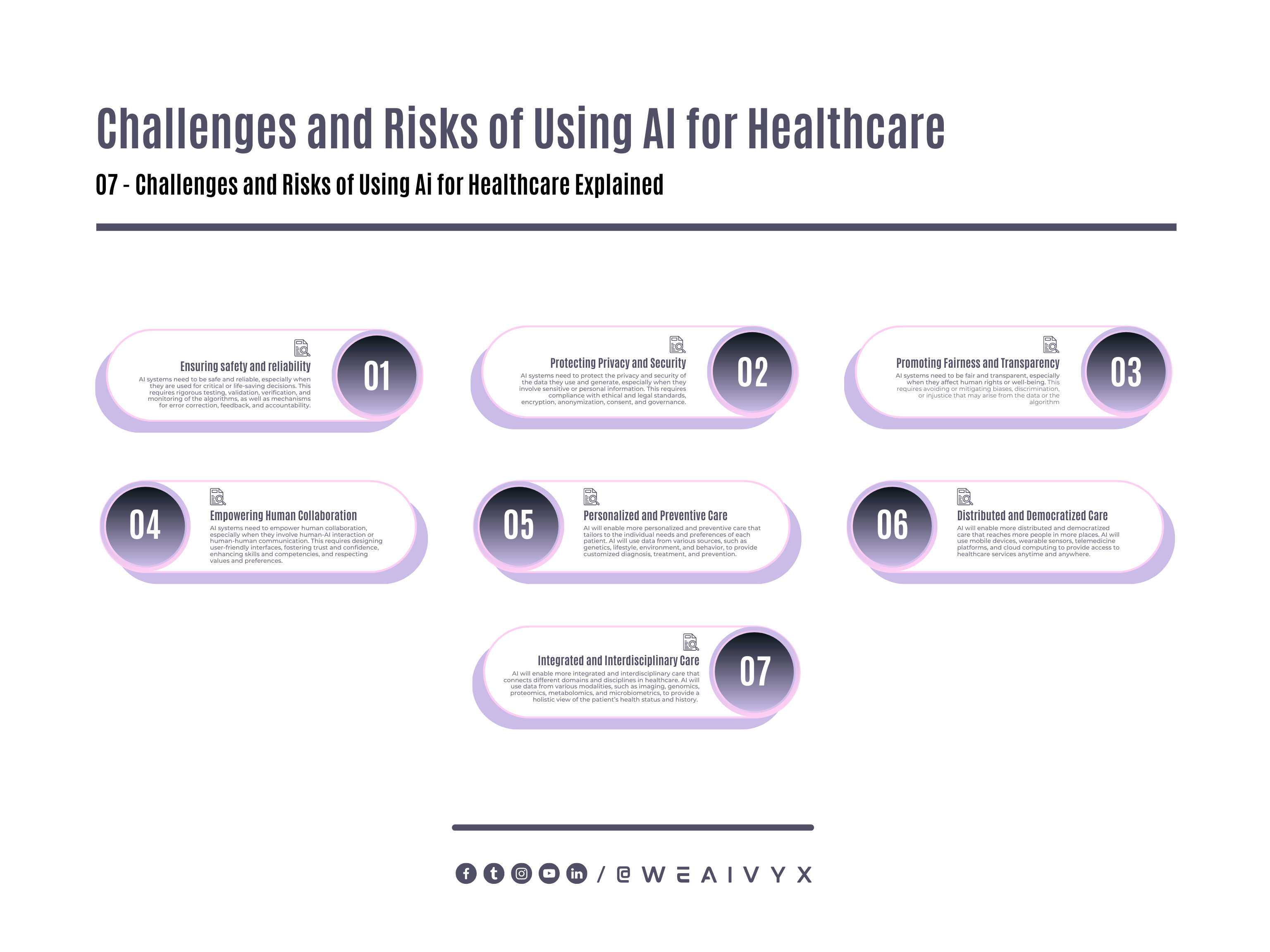
Some of the challenges and risks of using AI for healthcare include:
Ensuring safety and reliability
AI systems need to be safe and reliable, especially when they are used for critical or life-saving decisions.
This requires rigorous testing, validation, verification, and monitoring of the algorithms, as well as mechanisms for error correction, feedback, and accountability.
Protecting Privacy and Security
AI systems need to protect the privacy and security of the data they use and generate, especially when they involve sensitive or personal information.
This requires compliance with ethical and legal standards, encryption, anonymization, consent, and governance.
Promoting Fairness and Transparency
AI systems need to be fair and transparent, especially when they affect human rights or well-being.
This requires avoiding or mitigating biases, discrimination, or injustice that may arise from the data or the algorithm, as well as providing explanations, justifications, or interpretations of the algorithm’s decisions.
Empowering Human Collaboration
AI systems need to empower human collaboration, especially when they involve human-AI interaction or human-human communication.
This requires designing user-friendly interfaces, fostering trust and confidence, enhancing skills and competencies, and respecting values and preferences.
Personalized and Preventive Care
AI will enable more personalized and preventive care that tailors to the individual needs and preferences of each patient.
AI will use data from various sources, such as genetics, lifestyle, environment, and behavior, to provide customized diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
AI will also help monitor and manage chronic conditions, predict and prevent potential complications, and promote wellness and healthy habits.
Distributed and Democratized Care
AI will enable more distributed and democratized care that reaches more people in more places.
AI will use mobile devices, wearable sensors, telemedicine platforms, and cloud computing to provide access to healthcare services anytime and anywhere.
AI will also help empower patients and consumers to take more control and ownership of their health data and decisions, as well as engage with online communities and networks for support and guidance.
Integrated and Interdisciplinary Care
AI will enable more integrated and interdisciplinary care that connects different domains and disciplines in healthcare.
AI will use data from various modalities, such as imaging, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and microbiometrics, to provide a holistic view of the patient’s health status and history.
AI will also help bridge the gaps between different specialties, sectors, and stakeholders in healthcare, such as primary care, specialty care, public health, research, education, policy, and industry.
Conclusion
AI is a powerful and promising technology that can enhance and assist human doctors in medical diagnosis.
AI can provide faster, more accurate, more accessible, more scalable, and more innovative diagnoses than human doctors.
However, AI also has some limitations and challenges that need to be addressed, such as trust, communication, regulation, education, and evaluation.
AI should not be seen as a replacement for human doctors, but rather as a tool or a partner that can augment and complement them.
We hope you enjoyed this blog post and learned something new and useful. If you have any questions, comments, or feedback, please feel free to share them below.
We would love to hear from you and learn from your perspective. Thank you for reading and stay tuned for more blog posts on AI and medicine.
