AI is one of the most fascinating and powerful technologies of our time. It can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, decision-making, and natural language processing.
It can also learn from data and feedback, and improve its performance without being explicitly programmed.
But how independent is AI from human support?
Can AI exist without humans creating, developing, testing, or using it?
And what are the implications of having AI that can operate without human intervention or supervision?
In this article, we will explore these questions and provide some insights and perspectives on the relationship between AI and humans.
We will also discuss the benefits and challenges of having AI that can work with or without human support, and provide some examples of AI applications that can function online or offline.
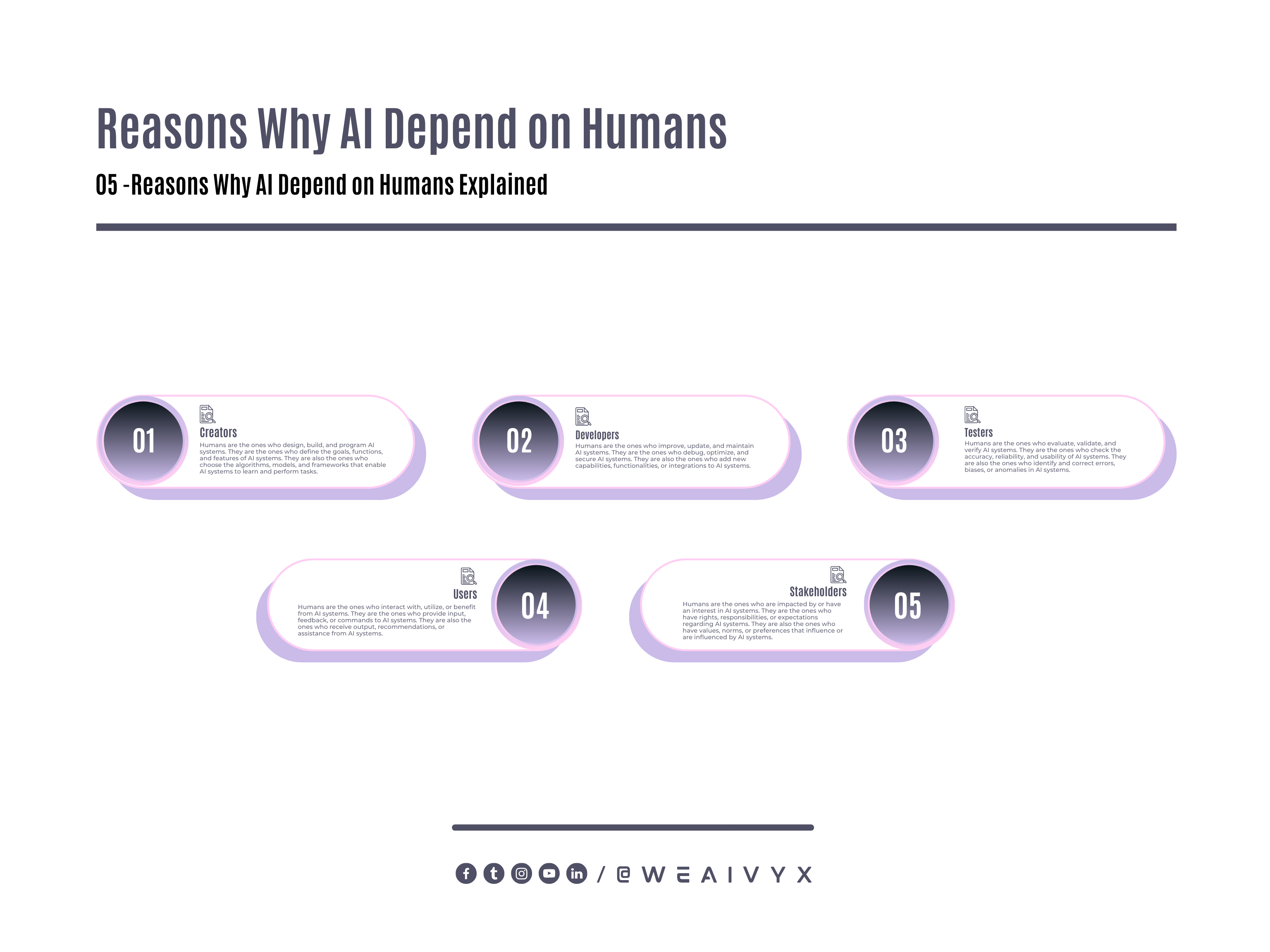
What is the Role of Humans in AI?
Humans play a vital role in AI, as they are the ones who create, develop, test, and use AI systems.
Humans are also the ones who provide data, feedback, or guidance to AI systems, and who benefit from or are affected by AI systems.
Here are some of the roles that humans have in AI:
Creators
Humans are the ones who design, build, and program AI systems. They are the ones who define the goals, functions, and features of AI systems.
They are also the ones who choose the algorithms, models, and frameworks that enable AI systems to learn and perform tasks.
Developers
Humans are the ones who improve, update, and maintain AI systems. They are the ones who debug, optimize, and secure AI systems.
They are also the ones who add new capabilities, functionalities, or integrations to AI systems.
Testers
Humans are the ones who evaluate, validate, and verify AI systems. They are the ones who check the accuracy, reliability, and usability of AI systems.
They are also the ones who identify and correct errors, biases, or anomalies in AI systems.
Users
Humans are the ones who interact with, utilize, or benefit from AI systems. They are the ones who provide input, feedback, or commands to AI systems.
They are also the ones who receive output, recommendations, or assistance from AI systems.
Stakeholders
Humans are the ones who are impacted by or have an interest in AI systems. They are the ones who have rights, responsibilities, or expectations regarding AI systems.
They are also the ones who have values, norms, or preferences that influence or are influenced by AI systems.
Can AI Work Without Human Support?
The answer to this question depends on what type of AI we are talking about, and what purpose we are using it for.
Generally speaking, there are two scenarios: online AI and offline AI.
Online AI is when the machine needs human support to access data or communicate with other machines or humans.
For example, online AI can be used to provide personalized recommendations based on user behavior or preferences collected from online platforms or services.
Offline AI is when the machine does not need human support to access data or communicate with other machines or humans.
For example, offline AI can be used to provide face recognition based on local data stored on the device or camera.
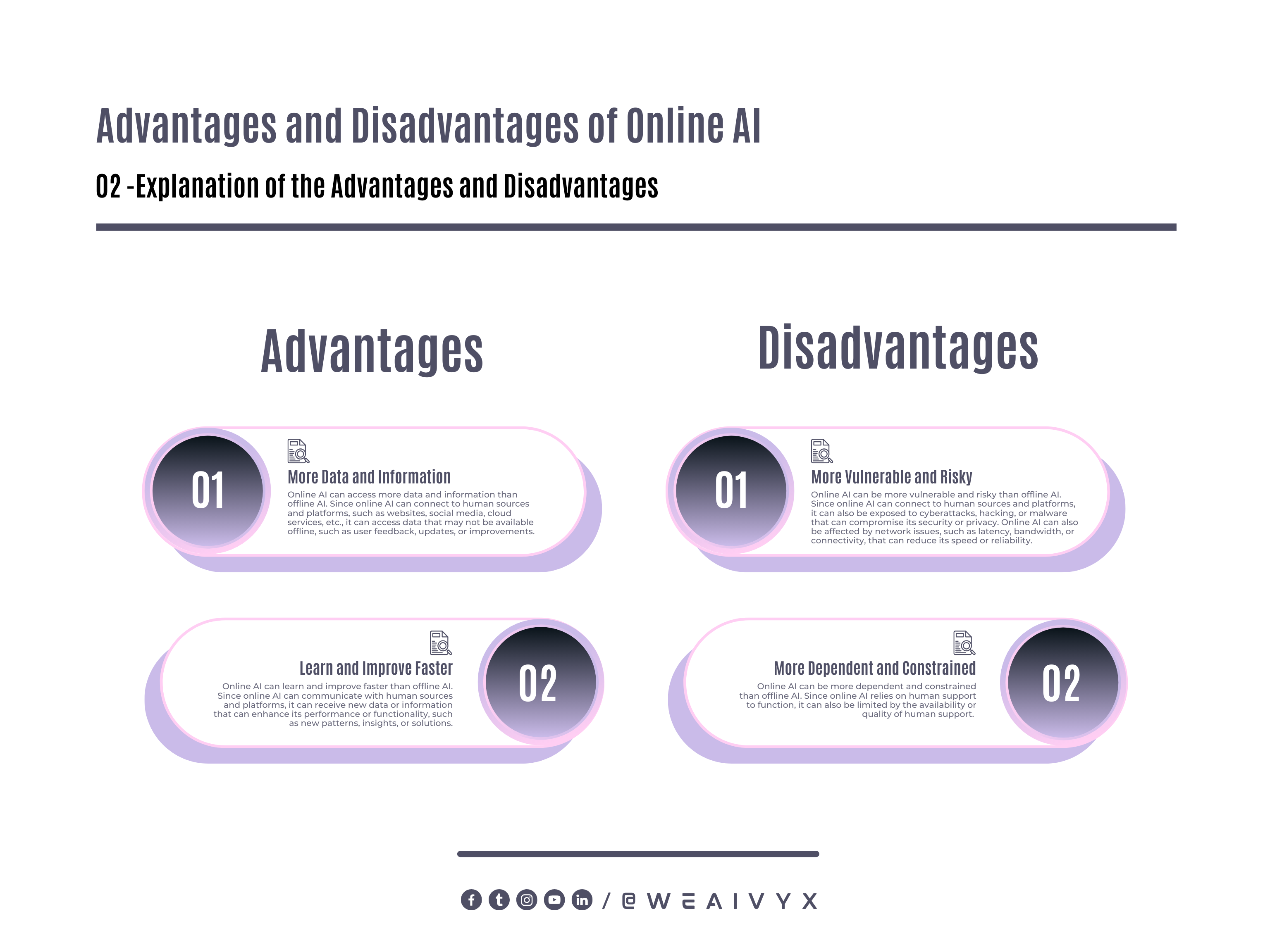
Online AI has some advantages and disadvantages compared to offline AI.
Here are some of them:
Pros
Online AI can access more data and information than offline AI.
Since online AI can connect to human sources and platforms, such as websites, social media, cloud services, etc.
It can access data that may not be available offline, such as user feedback, updates, or improvements.
Online AI can learn and improve faster than offline AI.
Since online AI can communicate with human sources and platforms.
It can receive new data or information that can enhance its performance or functionality, such as new patterns, insights, or solutions.
Cons
Online AI can be more vulnerable and risky than offline AI.
Since online AI can connect to human sources and platforms, it can also be exposed to cyberattacks, hacking, or malware that can compromise its security or privacy.
Online AI can also be affected by network issues, such as latency, bandwidth, or connectivity, that can reduce its speed or reliability.
Online AI can be more dependent and constrained than offline AI.
Since online AI relies on human support to function, it can also be limited by the availability or quality of human support.
Online AI can also be subject to regulations or policies that govern the use or distribution of data or information by humans, such as data protection laws, censorship, or geo-restrictions.
What Are Some Examples of Online and Offline AI?
Online and offline AI are not mutually exclusive categories of AI. Many AI applications can work both online and offline.
Depending on the settings or preferences of the users or developers. Here are some examples of online and offline AI applications:
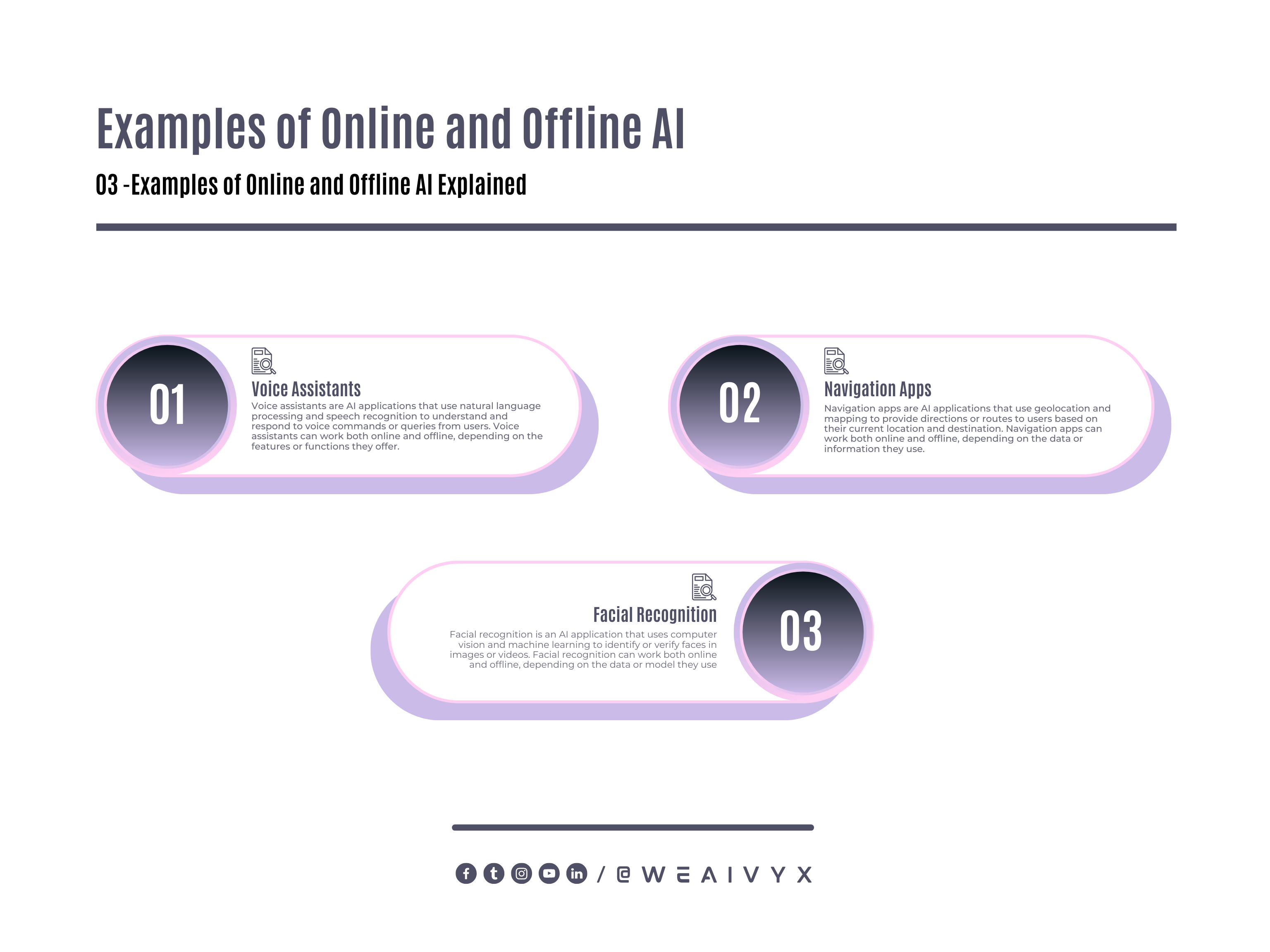
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants are AI applications that use natural language processing and speech recognition to understand and respond to voice commands or queries from users.
Voice assistants can work both online and offline, depending on the features or functions they offer.
For example, some voice assistants can perform basic tasks such as setting alarms, playing music, or making calls without human support, but they may need human support to perform more complex tasks such as searching the web, booking flights, or ordering food.
Navigation Apps
Navigation apps are AI applications that use geolocation and mapping to provide directions or routes to users based on their current location and destination.
Navigation apps can work both online and offline, depending on the data or information they use.
For example, some navigation apps can download maps and store them locally on the device for offline use without human support, but they may need human support to update traffic conditions, road closures, or public transit schedules.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition is an AI application that uses computer vision and machine learning to identify or verify faces in images or videos.
Facial recognition can work both online and offline, depending on the data or model they use
For example, some facial recognition systems can use local data stored on the device or camera for offline use without human support, but they may need human support to access cloud-based data or models for online use.
How to Use AI Responsibly and Ethically?
AI is a powerful and promising technology that can bring many benefits and opportunities to us and society.
However, it can also pose many challenges and risks that need to be addressed and managed carefully. Here are some tips on how to use AI responsibly and ethically:
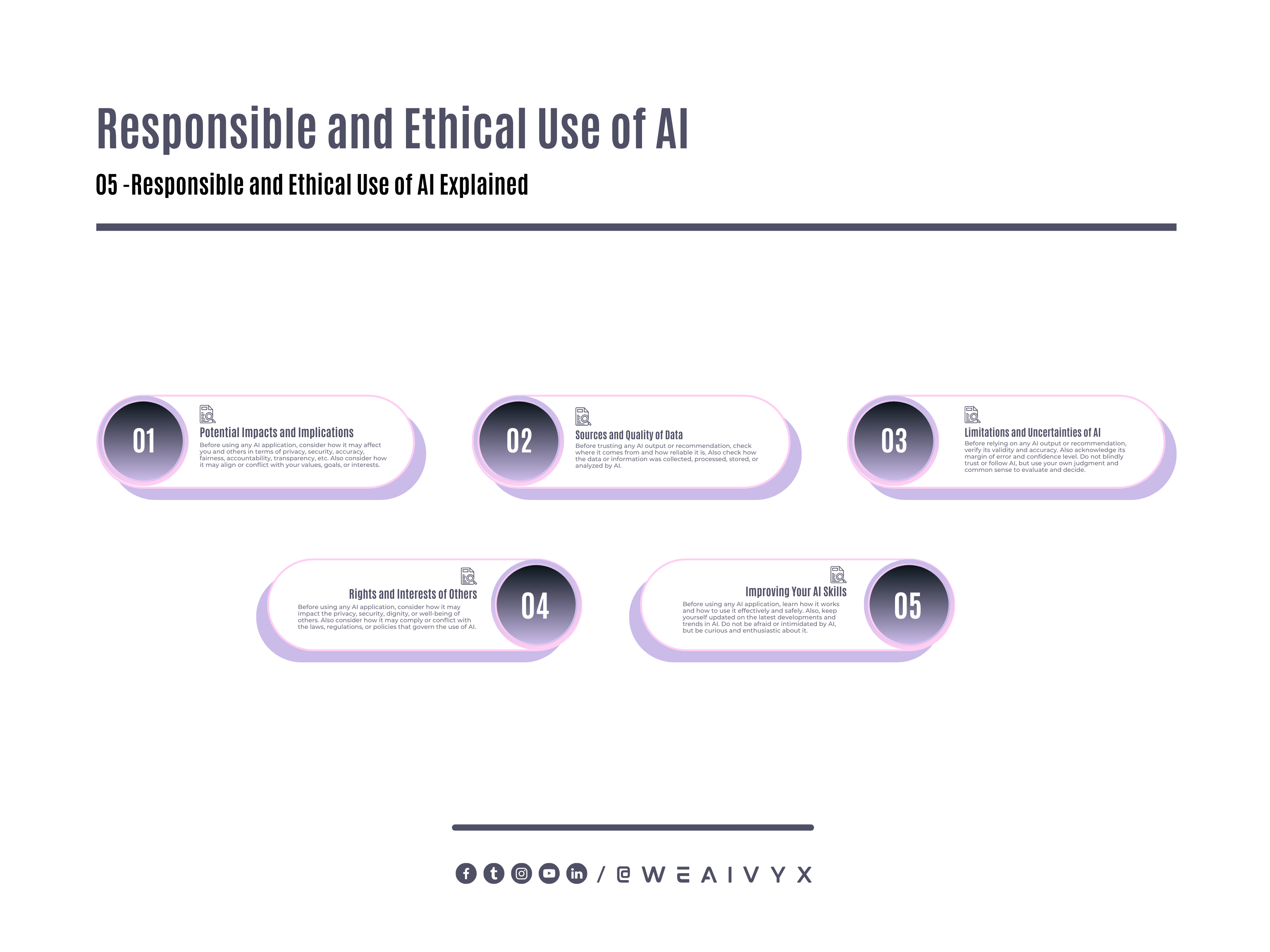
Be Aware of the Potential Impacts and Implications of Using AI
Before using any AI application, consider how it may affect you and others in terms of privacy, security, accuracy, fairness, accountability, transparency, etc.
Also consider how it may align or conflict with your values, goals, or interests.
Be Informed of the Sources and Quality of Data and Information Used by AI
Before trusting any AI output or recommendation, check where it comes from and how reliable it is.
Also check how the data or information was collected, processed, stored, or analyzed by AI.
Also check how the data or information was used or interpreted by AI, and whether it was biased, manipulated, or misrepresented.
Be Critical of the Limitations and Uncertainties of AI
Before relying on any AI output or recommendation, verify its validity and accuracy. Also, acknowledge its margin of error and confidence level.
Do not blindly trust or follow AI, but use your judgment and common sense to evaluate and decide.
Be Respectful of the Rights and Interests of Others Affected by AI
Before using any AI application, consider how it may impact the privacy, security, dignity, or well-being of others.
Also consider how it may comply or conflict with the laws, regulations, or policies that govern the use of AI.
Do not use AI to harm, deceive, or exploit others, but use it to help, support, or empower them.
Be Proactive in Learning and Improving Your AI Skills and Knowledge
Before using any AI application, learn how it works and how to use it effectively and safely. Also, keep yourself updated on the latest developments and trends in AI.
Do not be afraid or intimidated by AI, but be curious and enthusiastic about it.
Conclusion
AI is a technology that can work with or without human support, depending on the type of AI and the purpose of using it.
Online AI can access more data and information, learn and improve faster, but also be more vulnerable and risky, more dependent and constrained than offline AI.
Offline AI can be more robust and reliable, more efficient and scalable, but also more limited and rigid, more labor-intensive and costly than online AI.
AI is also a technology that can bring many benefits and opportunities, but also poses many challenges and risks that need to be addressed and managed carefully.
By understanding the role of humans in AI, and how to use AI responsibly and ethically, we can create more enjoyable, useful, and responsible AI experiences.
If you liked this article, please share it with your friends or colleagues who are interested in AI. If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below. I would love to hear from you!
