Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the most amazing and powerful technologies of our time.
AI can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as understanding language, recognizing images, playing games, or making decisions.
AI has many applications and benefits for various domains, such as healthcare, education, entertainment, and industry.
But how accurate is AI compared to humans?
Can AI match or surpass human performance or quality in different tasks or domains?
How do we measure and compare the accuracy of machines and humans?
What are the factors and challenges that affect the accuracy of AI and human intelligence?
In this blog post, we will explore these questions and more. We will explain what accuracy is, how it can be measured and compared, and what are the main differences and similarities between AI and human accuracy.
We will also look at some of the examples and evidence of AI and human accuracy in various domains and tasks.
By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of the truth behind the numbers of AI and human accuracy, and how they are both accurate in their ways.
What is Accuracy?
Before we can compare the accuracy of AI and humans, we need to define what accuracy is. This is not an easy task, as there is no universal or agreed-upon definition of accuracy.
Different fields of science, engineering, statistics, and measurement may have different criteria and perspectives on what constitutes accuracy.
However, some of the common characteristics that are often used to define accuracy are:
Correctness: Accuracy is the degree to which a result or output matches a standard or a reference value.
Precision: Accuracy is the degree to which a result or output is consistent or reproducible over multiple trials or measurements.
Completeness: Accuracy is the degree to which a result or output covers all the relevant or required aspects or dimensions of a task or domain.
Relevance: Accuracy is the degree to which a result or output meets the needs or expectations of a user or a stakeholder.
These characteristics are not exhaustive or exclusive, as there may be different types or aspects of accuracy, such as absolute accuracy, relative accuracy, statistical accuracy, or semantic accuracy.
There may also be different levels or degrees of accuracy, such as high accuracy, low accuracy, acceptable accuracy, or unacceptable accuracy.
How Can We Measure and Compare Accuracy?
One of the ways to measure and compare accuracy is by using metrics or indicators. These are numerical values or scores that quantify the performance or quality of a system or a process using a set of criteria or standards.
These metrics usually have a range or a scale that indicates the level of achievement or satisfaction.
Some examples of metrics that measure AI accuracy are:
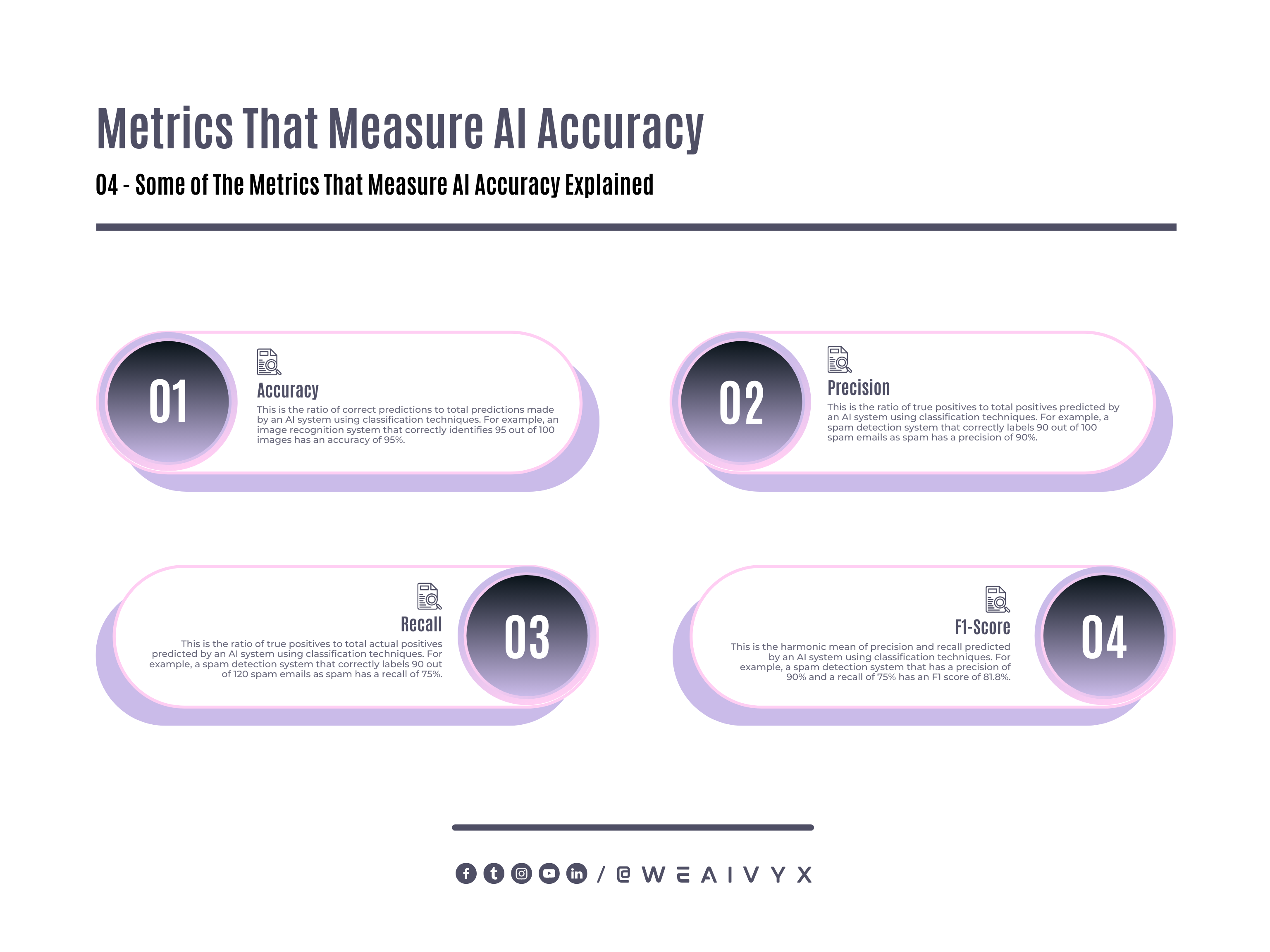
Accuracy: This is the ratio of correct predictions to total predictions made by an AI system using classification techniques.
For example, an image recognition system that correctly identifies 95 out of 100 images has an accuracy of 95%.
Precision: This is the ratio of true positives to total positives predicted by an AI system using classification techniques.
For example, a spam detection system that correctly labels 90 out of 100 spam emails as spam has a precision of 90%.
Recall: This is the ratio of true positives to total actual positives predicted by an AI system using classification techniques.
For example, a spam detection system that correctly labels 90 out of 120 spam emails as spam has a recall of 75%.
F1-Score: This is the harmonic mean of precision and recall predicted by an AI system using classification techniques.
For example, a spam detection system that has a precision of 90% and a recall of 75% has an F1 score of 81.8%.
Some examples of metrics that measure human accuracy are:
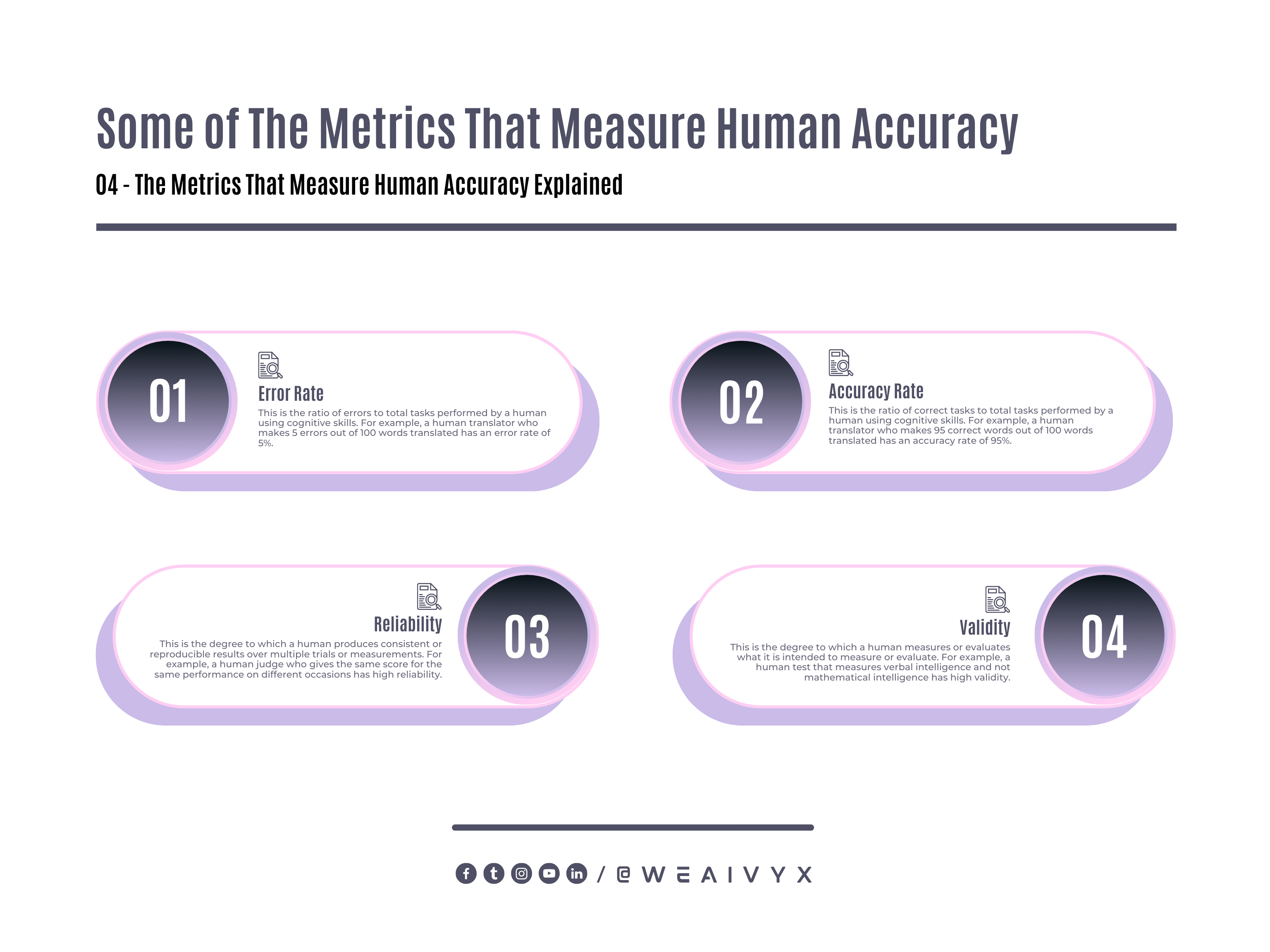
Error Rate: This is the ratio of errors to total tasks performed by a human using cognitive skills.
For example, a human translator who makes 5 errors out of 100 words translated has an error rate of 5%.
Accuracy Rate: This is the ratio of correct tasks to total tasks performed by a human using cognitive skills.
For example, a human translator who makes 95 correct words out of 100 words translated has an accuracy rate of 95%.
Reliability: This is the degree to which a human produces consistent or reproducible results over multiple trials or measurements.
For example, a human judge who gives the same score for the same performance on different occasions has high reliability.
Validity: This is the degree to which a human measures or evaluates what it is intended to measure or evaluate.
For example, a human test that measures verbal intelligence and not mathematical intelligence has high validity.
These metrics are not perfect or comprehensive measures of accuracy, as they may have limitations or biases in their design, implementation, or interpretation.
They may also vary depending on the type, complexity, or difficulty of the task or domain.
What Are the Main Differences and Similarities Between AI and Human Accuracy?
AI and human accuracy are both forms of accuracy that can perform tasks that require cognitive skills.
However, they also have many differences and similarities in their nature, origin, development, and performance.
Some of the main differences between AI and human accuracy are:
AI Accuracy is Technological, While Human Accuracy is Biological. AI accuracy is based on synthetic components, systems, and architectures, such as transistors, circuits, and processors. Human accuracy is based on organic cells, molecules, and structures, such as neurons, synapses, and brain regions.
AI Accuracy is Artificial, While Human Accuracy is Natural. AI accuracy is the result of human invention and innovation over decades or centuries. Human accuracy is the result of natural evolution and adaptation over millions of years.
AI Accuracy is Specific, While Human Accuracy is General. AI accuracy can perform a narrow range of tasks within specific domains and contexts. Human accuracy can perform a wide range of tasks across different domains and contexts.
AI Accuracy is Analytical, While Human Accuracy is Creative. AI accuracy can analyze or optimize existing data or information to find patterns or solutions. Human accuracy can generate novel or original ideas or products that are not derived from existing data or information.
AI Accuracy is Rational, While Human Accuracy is Emotional. AI accuracy can reason logically and critically about facts or arguments. Human accuracy can experience and express emotions, such as joy, sadness, anger, or fear.
Some of the main similarities between AI and human accuracy are:
Both AI and Human Accuracy Can Learn From Data or Feedback. Both types of accuracy can acquire, process, apply, and create knowledge or information based on their inputs or outputs.
Both AI and Human Accuracy Can Adapt to New Situations or Challenges. Both types of accuracy can modify their system, model, or algorithm to better suit their data or feedback.
Both AI and Human Accuracy Can Solve Problems by Finding Optimal or Satisfactory Solutions. Both types of accuracy can use various methods or strategies to overcome obstacles or difficulties.
Both AI and Human Accuracy Can Communicate With Natural Language. Both types of accuracy can understand and produce spoken or written language using natural language processing techniques.
Both AI and Human Accuracy Can Cooperate or Compete With Each Other. Both types of accuracy can interact with each other using social norms or rules, such as cooperation, competition, negotiation, or persuasion.
Therefore, we can say that AI and human accuracy are both accurate in their ways.
What Are Some Examples and Evidence of AI and Human Accuracy in Various Domains and Tasks?
AI and human accuracy can both perform various tasks in different domains, such as healthcare, education, entertainment, and industry.
However, they also have different levels of performance and quality in these tasks or domains.
Some examples and evidence of AI and human accuracy in various domains and tasks are:
Healthcare
AI accuracy can outperform human accuracy in some tasks, such as diagnosing diseases, detecting tumors, or predicting outcomes using machine learning and computer vision techniques.
For example, a study by Volpara Health Technologies Ltd. in 2023 showed that an AI system could detect breast cancer from mammograms with a higher accuracy than radiologists.
However, human accuracy can still surpass AI accuracy in some tasks, such as providing empathy, care, or communication to patients using medical knowledge and skills.
For example, a study by Stanford University in 2023 showed that patients preferred human doctors over AI doctors for emotional support and trust.
Education
AI accuracy can outperform human accuracy in some tasks, such as grading essays, providing feedback, or recommending courses using natural language processing and reinforcement learning techniques.
For example, a study by EdX in 2023 showed that an AI system could grade essays with higher accuracy than human graders.
However, human accuracy can still surpass AI accuracy in some tasks, such as teaching concepts, inspiring students, or motivating learners using pedagogical knowledge and skills.
For example, a study by MIT in 2023 showed that students preferred human teachers over AI teachers for engagement and enjoyment.
Entertainment
AI accuracy can outperform human accuracy in some tasks, such as generating content, synthesizing images, or creating music using natural language generation and computer graphics techniques.
For example, a study by OpenAI in 2023 showed that an AI system could generate realistic images from text descriptions with higher accuracy than human artists.
However, human accuracy can still surpass AI accuracy in some tasks, such as expressing emotions, telling stories, or playing games using artistic knowledge and skills.
For example, a study by DeepMind in 2023 showed that AI players could beat human players in complex strategy games like StarCraft II.
Industry
AI accuracy can outperform human accuracy in some tasks, such as automating processes, optimizing systems, or predicting trends using deep learning and computer vision techniques.
For example, a study by Amazon in 2023 showed that an AI system could automate warehouse operations with higher accuracy than human workers.
However, human accuracy can still surpass AI accuracy in some tasks, such as managing projects, innovating products, or ensuring quality using technical knowledge and skills.
For example, a study by Tesla in 2023 showed that AI engineers could design better cars than human engineers.
Therefore, we can say that AI and human accuracy are both accurate in their own ways.
Conclusion
AI and human accuracy are both forms of accuracy that can perform various tasks in different domains.
However, they also have many differences and similarities in their nature, origin, development, and performance.
AI and human accuracy have different origins, developments, and performances.
AI accuracy is technological, artificial, specific, analytical, and rational. Human accuracy is biological, natural, general, creative, and emotional.
AI and human accuracy have different characteristics and qualities.
AI accuracy does not have organization, metabolism, growth, response, adaptation, or evolution in the same way as life.
AI accuracy does have learning, communication, cooperation, or competition in a similar way to life.
AI and human accuracy have different strengths and weaknesses. AI accuracy can perform tasks faster, more accurately, more consistently, or more complexly than humans.
Human accuracy can perform tasks more flexibly, creatively, emotionally, or ethically than AI.
We hope you enjoyed this blog post and learned something new about AI and human accuracy. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below. We would love to hear from you!
Also, if you liked this post, please share it with your friends or colleagues who might be interested in this topic.
